
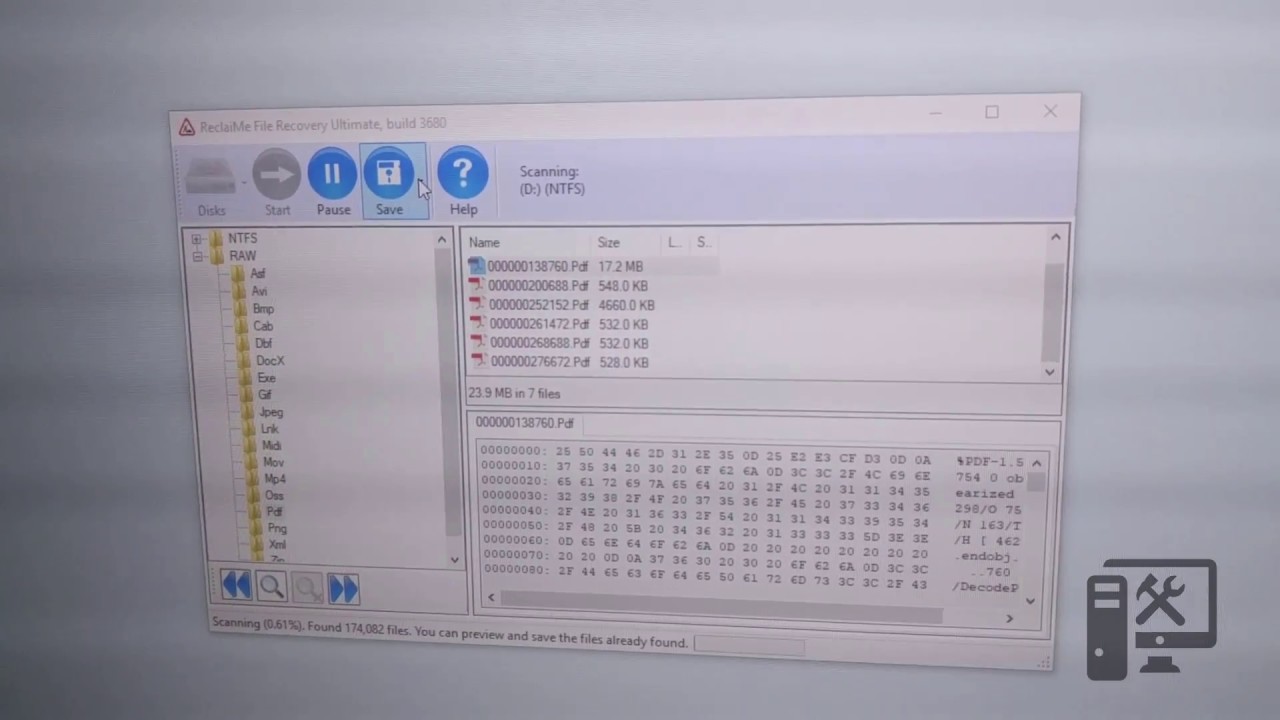
Fault tolerance, however, is still ensured by the good old RAID5 technology which the md driver is responsible for.
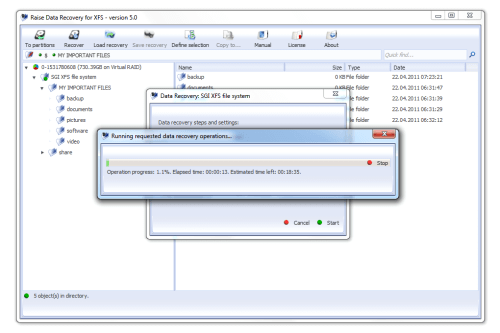
At the moment, all RAID level implementations in BTRFS except RAID5 work reliable that's why modern NETGEAR NASes use BTRFS only to create JBOD, thus replacing the LVM layer. For example, it is possible to take two devices and create an equivalent of RAID0 or RAID1 by means of BTRFS alone.īTRFS supports almost all RAID levels – JBOD, RAID1, RAID0, RAID5 - with varying degrees of reliability. However, it is important to understand that BTRFS is not just a filesystem but a hybrid of filesystem and volume manager. When recovering data from a NAS working under one of these schemes, one recovers each layer one by one the last layer (filesystem recovery) is fully studied because of the EXT and XFS age and is recovered pretty well.īTRFS filesystem has much more features including snapshots, compression, data and metadata checksumming. The 2-layer and 3-layer schemes are quite reliable and time-tested however, they are not that feature rich. Typically, it is an EXT filesystem family (EXT3 or EXT4) some vendors opted for XFS, for example in Buffalo NAS models. In the 3-layer scheme, LVM provides a possibility to expand an array by adding or replacing disks with larger ones without filesystem reconstruction, thus eliminating the need to backup and restore a NAS during expansion.Īs for the filesystems, any Linux filesystem can be used since NASes usually operate under Linux operating system. Synology NASes and NETGEAR NASes with in X-RAID2 mode utilize the 3-layer scheme.

Such a scheme is used in QNAP NASes and NETGEAR NASes configured in Flex-RAID mode.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
